What is Cloud Computing? A Comprehensive Guide

The cloud is a key component of the world’s digital infrastructure, powering everything from messaging apps and banking to media streaming and e-commerce. Many websites and apps we use to shop, stream, search, and socialize over the Internet rely on the cloud to reliably serve us data within milliseconds.
In this article, you will understand what exactly cloud computing is, including its core principles, deployment models, the different types of cloud services, and much more. Enjoy your reading!
Cloud computing: a quick overview 💡
Definition: Cloud computing delivers computing services (e.g., servers, storage, databases, and software) over the internet. This allows users to access resources on demand without managing physical hardware.
How it works: Instead of owning data centers or servers, users (businesses and individuals) rent access to computing power from cloud providers, paying only for what they use.
Benefits:
- Scalability: Easily scale resources up or down based on demand.
- Cost Savings: Pay only for the resources you use.
- Accessibility: Access data and applications from anywhere.
- Security: Providers prioritize robust security measures to protect data.
From on-premise IT to the cloud: a paradigm shift
Before the advent of the cloud, most businesses relied on on-premise IT infrastructure, requiring significant investments in physical servers, storage, and networking equipment. While this gave organizations full control over their systems, it came with high upfront costs, ongoing maintenance expenses, and the need for dedicated IT teams. Scaling this infrastructure was cumbersome and slow, often leading to wasted resources during periods of low demand or insufficient capacity during growth spurts.
The need for greater flexibility and cost efficiency drove the shift to cloud computing. Cloud services offer businesses scalable, on-demand resources without the burden of managing physical hardware. Providers also delivered robust security, regular updates, and data redundancy, ensuring reliability and freeing organizations to focus on innovation rather than IT maintenance. These advantages made cloud computing the preferred choice for modern businesses.
Understanding cloud computing: a beginner’s overview
While cloud computing might initially seem complex, it’s really a straightforward concept: providing computing resources conveniently over the Internet.
Definition of cloud computing
Cloud computing refers to providing computing services such as servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and more over the internet. Users access these resources pay-as-you-go, eliminating the need for costly on-premises infrastructure. Think of it as renting a fully equipped office rather than owning the building.
The term “cloud” represents a network of remote servers hosted on the internet, designed to store and process data. Cloud computing enables businesses to scale their operations seamlessly and focus on their core goals without the overhead of managing physical servers.
Types of cloud computing
The cloud ecosystem is diverse, offering different cloud computing models based on the deployment and usage approach. Understanding these types can help you determine the right solution for your needs.
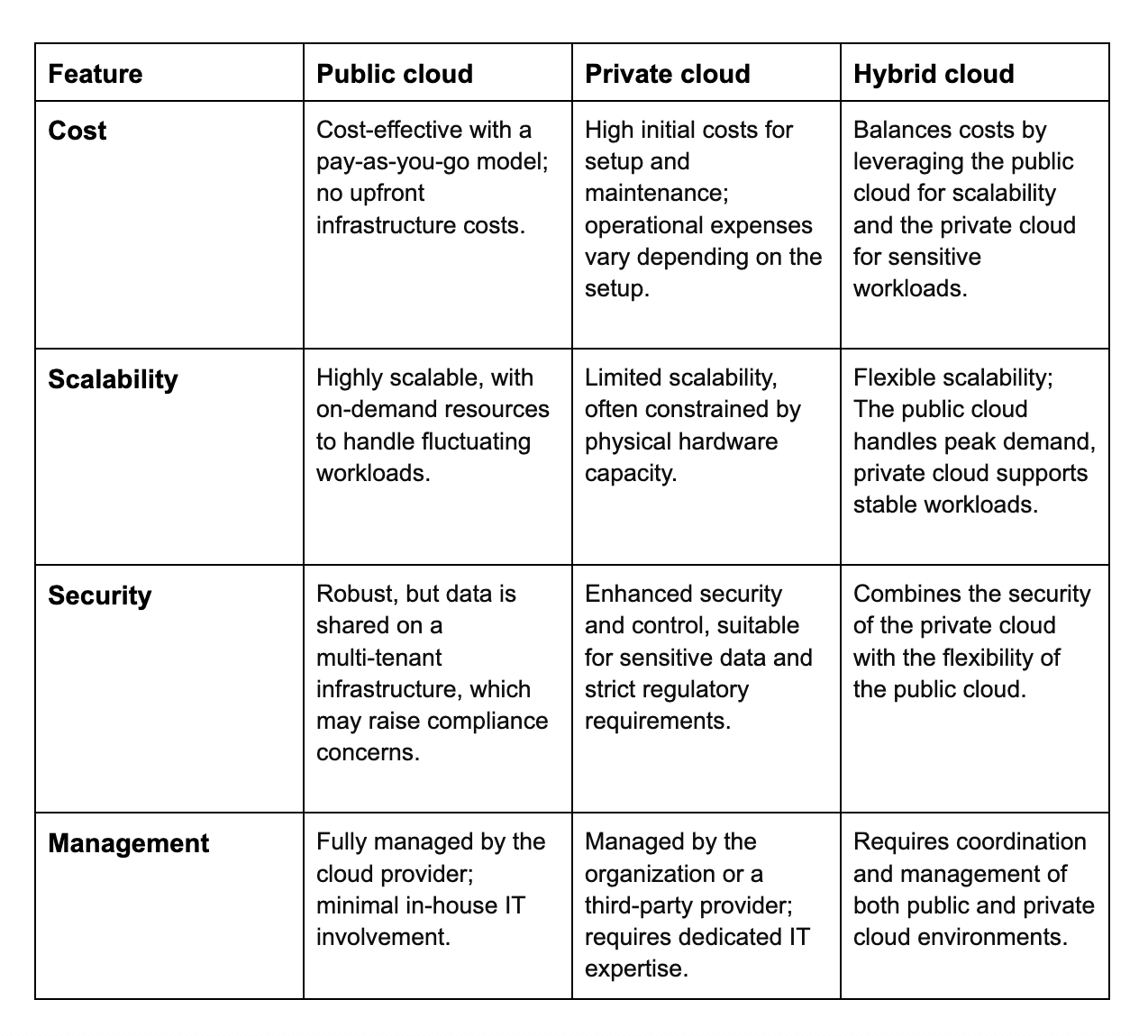
Public cloud
A public cloud is managed by third-party service providers, who own and operate the infrastructure. Users share the same resources (e.g., storage, virtual machines) with other customers, making this a cost-effective option. Public cloud offers like Scaleway’s Elastic Metal or Object Storage are ideal for businesses seeking scalable, easy-to-deploy services without the burden of managing hardware.
Private cloud
A private cloud, on the other hand, is dedicated to a single organization. It offers greater control and customization options but is more expensive to set up and maintain. Businesses that deal with sensitive data or have strict regulatory requirements often prefer private clouds for their enhanced security and compliance capabilities.
Hybrid cloud and multi-cloud environments
A hybrid cloud integrates both public and private clouds, allowing businesses to move workloads between the two as needed. This approach is valuable for companies that require the flexibility of the public cloud for some operations but need the privacy of a private cloud for others. Multi-cloud environments involve using services from multiple cloud providers, which helps to avoid vendor lock-in and improve resilience.
Different Types of Cloud Computing Services
Cloud services fall into several categories depending on the level of control and management offered to the customer. Let's explore three main service models: IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS.
IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)
IaaS provides the foundational building blocks for cloud computing, offering virtualized computing resources over the internet. Users get access to servers, storage, and networking resources without managing physical infrastructure. Scaleway's Compute Instances is a prime example of IaaS, where businesses can quickly scale their infrastructure up or down.
PaaS (Platform as a Service)
PaaS offers a development environment where users can build, deploy, and manage applications without dealing with underlying infrastructure. Developers can focus on coding while the platform handles the server management, operating systems, and databases. Scaleway’s Kubernetes Kapsule is a popular PaaS offering that simplifies container orchestration for developers.
SaaS (Software as a Service)
SaaS delivers complete software applications over the internet, typically on a subscription basis. Users access the software through a web browser, eliminating the need for local installations. Popular SaaS applications include Google Workspace, Salesforce, and Slack.
Benefits of cloud computing for businesses
Now that you understand what cloud computing is, let’s look at some of the major benefits it offers to businesses of all sizes.
Flexibility
Cloud computing allows businesses to scale their resources dynamically based on current demand. Instead of investing heavily in physical infrastructure that may become obsolete or underutilized, organizations can pay only for what they use, providing significant cost savings.
Accessibility and mobility provided by the Cloud
Cloud services are accessible from anywhere with an internet connection, enabling remote work and mobility. Whether employees work from home, on the go, or across different continents, they can access the same resources and collaborate seamlessly in real time.
Security and Data Privacy in the Cloud
One of the common misconceptions about the cloud is that it’s less secure than on-premise infrastructures. However, major cloud providers like Scaleway invest heavily in security measures, including encryption, identity management, and compliance certifications, ensuring that data is stored and transmitted securely. Many businesses leverage the cloud to enhance security and mitigate risks.
Examples of Cloud Computing Use Cases
Cloud computing is incredibly versatile, supporting a wide array of applications. Here are some everyday use cases:
- Cloud storage for personal files or enterprise data
- Web hosting for websites, applications, and e-commerce platforms
- Big data analytics for processing large datasets in real-time
- Disaster recovery solutions to back up and restore critical data.
Cloud Computing for Startups
For startups, cloud computing offers the ability to launch quickly without significant capital investments in IT infrastructure. Scaleway’s startup programs provide resources, credits, and mentorship to help new businesses accelerate their growth in the cloud.
Enterprise-Level Cloud Solutions
Large enterprises benefit from the cloud by optimizing their operations, reducing IT costs, and driving innovation. Enterprises often adopt hybrid or multi-cloud strategies to ensure flexibility, compliance, and efficiency.
Industry-Specific Applications
Cloud computing has transformed various industries by enabling innovative solutions and improving operational efficiency. In healthcare, it allows secure storage and management of patient records. In the retail sector, cloud platforms power personalized shopping experiences by leveraging customer data for targeted marketing and inventory optimization. Similarly, cloud-based solutions facilitate online learning in education, making interactive content and collaboration tools accessible to students and educators worldwide. These examples highlight how the cloud fosters growth across diverse fields, enabling organizations to meet the evolving demands of their industries.
Scaleway: Major Cloud Computing Provider in Europe
Scaleway is one of the leading cloud providers in Europe, known for its sustainable infrastructure, high-performance cloud services, and transparent pricing. Scaleway supports businesses of all sizes across the continent.
Scaleway’s extensive product portfolio includes:
- Compute services: Offering a range of virtual instances, including cost-optimized, workload-optimized, and GPU Instances, Scaleway caters to various computational requirements
- Storage solutions: Providing Object Storage, Block Storage, and cold storage options, Scaleway ensures data is securely stored and readily accessible
- Networking services: Features such as Virtual Private Cloud (VPC), Load Balancers, and Public Gateways enable businesses to build secure and efficient network architectures
- AI and Machine Learning: Scaleway offers high-performance GPU-based infrastructures, facilitating the development and scaling of AI projects from inception to deployment.
Future Trends in Cloud Computing
The cloud landscape continues to evolve, with several exciting trends shaping the industry's future.
AI and Machine Learning in the Cloud
AI and machine learning applications are increasingly being hosted on cloud platforms, allowing businesses to harness the power of these technologies without needing specialized infrastructure. Cloud providers like Scaleway offer more advanced AI and ML tools to democratize access to these powerful technologies.
Edge Computing and its Impact on the Cloud
Edge computing is another game-changer, allowing data to be processed closer to where it’s generated, reducing latency and improving performance. This is especially relevant in industries like IoT, where real-time data processing is critical. As edge computing matures, it will complement traditional cloud computing to create faster, more efficient networks.
Sustainability and Green Cloud Computing
Sustainable cloud computing is paving the way for a greener future by focusing on energy efficiency, renewable energy, and smarter resource use. Scaleway is at the forefront of this shift with initiatives like its eco-friendly DC5 data center and the innovative Environmental Footprint Calculator, empowering users to track their emissions and make greener choices, such as opting for energy-efficient servers. By adopting eco-conscious practices and optimizing workloads, the cloud industry plays a crucial role in reducing its environmental footprint and supporting global sustainability efforts.
A closing thought
Cloud computing has revolutionized how businesses and individuals access, store, and process information, offering unmatched flexibility and innovation through scalable, on-demand resources. Whether through public, private, or hybrid models, it empowers organizations to optimize operations, enhance collaboration, and drive growth.
As adoption expands, sustainability and responsible usage have become key priorities. Providers like Scaleway are leading the way with energy-efficient solutions and renewable energy initiatives. Looking ahead, the cloud will continue to drive progress, balancing technological advancement with the need for sustainability and data privacy, shaping a smarter and more connected future.