Migrating existing databases to a Database Instance
Managed Database for PostgreSQL and MySQL product provides reliable high-performance managed SQL database engines, both for PostgreSQL and MySQL. Using the service allows you to stay focused on the development of your applications and to benefit from Scaleway's expertise in the management of your database engines.
In this guide, you will learn how to migrate your existing databases on your Database Instances using an intermediate host.
This guide consists of two parts, depending on which database Engine your Instances are running:
- Database migration for PostgreSQL
- Database migration for MySQL
Before you start
To complete the actions presented below, you must have:
- A Scaleway account logged into the console
- Owner status or IAM permissions allowing you to perform actions in the intended Organization
- An SSH key
- A Database for PostgreSQL or MySQL
- An Instance available as an intermediate host for the migration
Database migration for PostgreSQL
Exporting the source database
- Connect to your Instance using SSH:
ssh root@<virtual_instance_ip> - Update the
aptpackage cache and upgrade the software already installed on the system:apt update && apt upgrade -y - We use
pg_dumpto dump the content of the database to migrate. It is included in the packagepostgresql-client-16. Install it using apt:apt install postgresql-client-16 - Dump the content of the originating database into a local SQL file on the Instance:
pg_dump --host=<host> --port=<port> --username=<user> --dbname=<database_name> --file=<filename>.sql
In the above command, replace the following values as follows:
-
<host>: The database server hosting the PostgreSQL database -
<port>: The TCP port on which the database server is listening (by default5432) -
<user>: The username used for the connection to the database server -
<database_name>: The name of the database to export -
<filename>: The name of the local file of the exported database
Preparing the Database for PostgreSQL
- Enter the Database section of the Scaleway console.
- Select your Database Instance from the list.
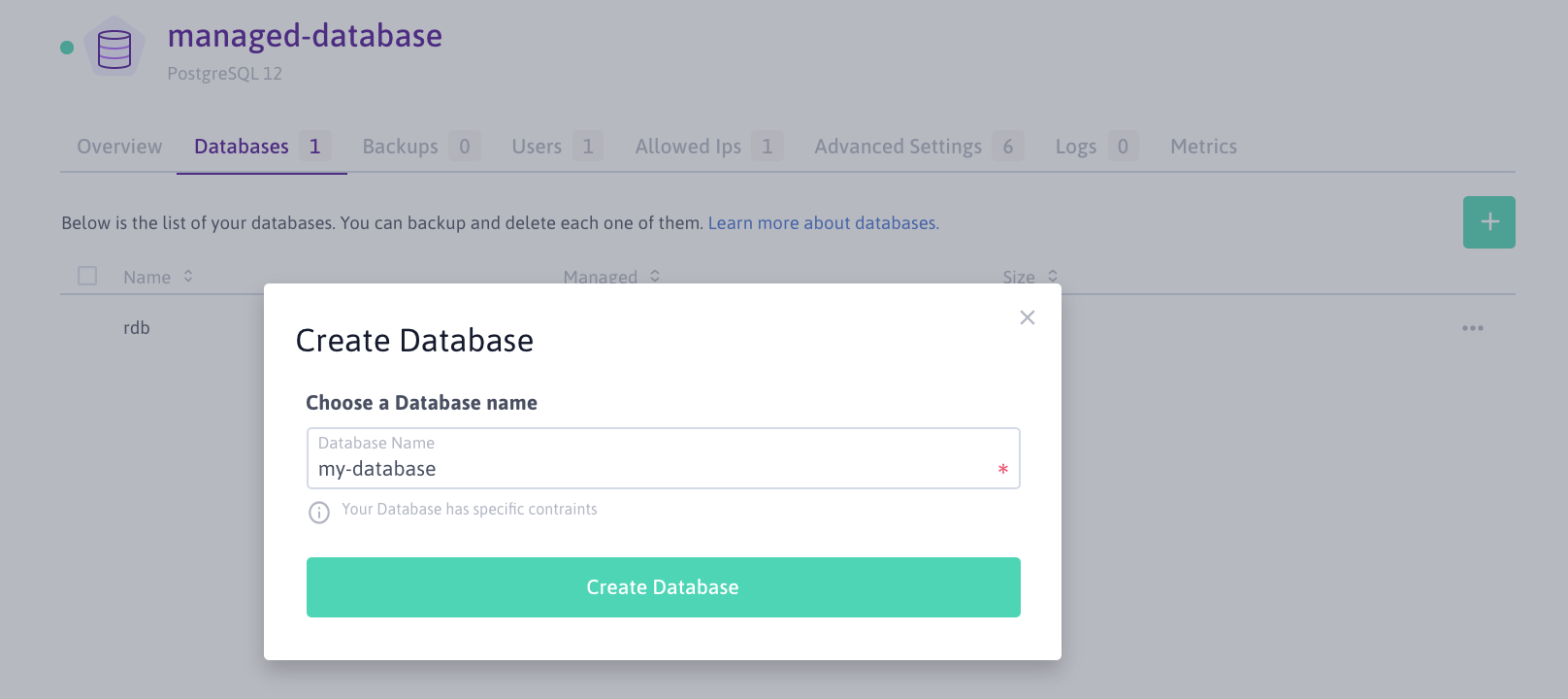
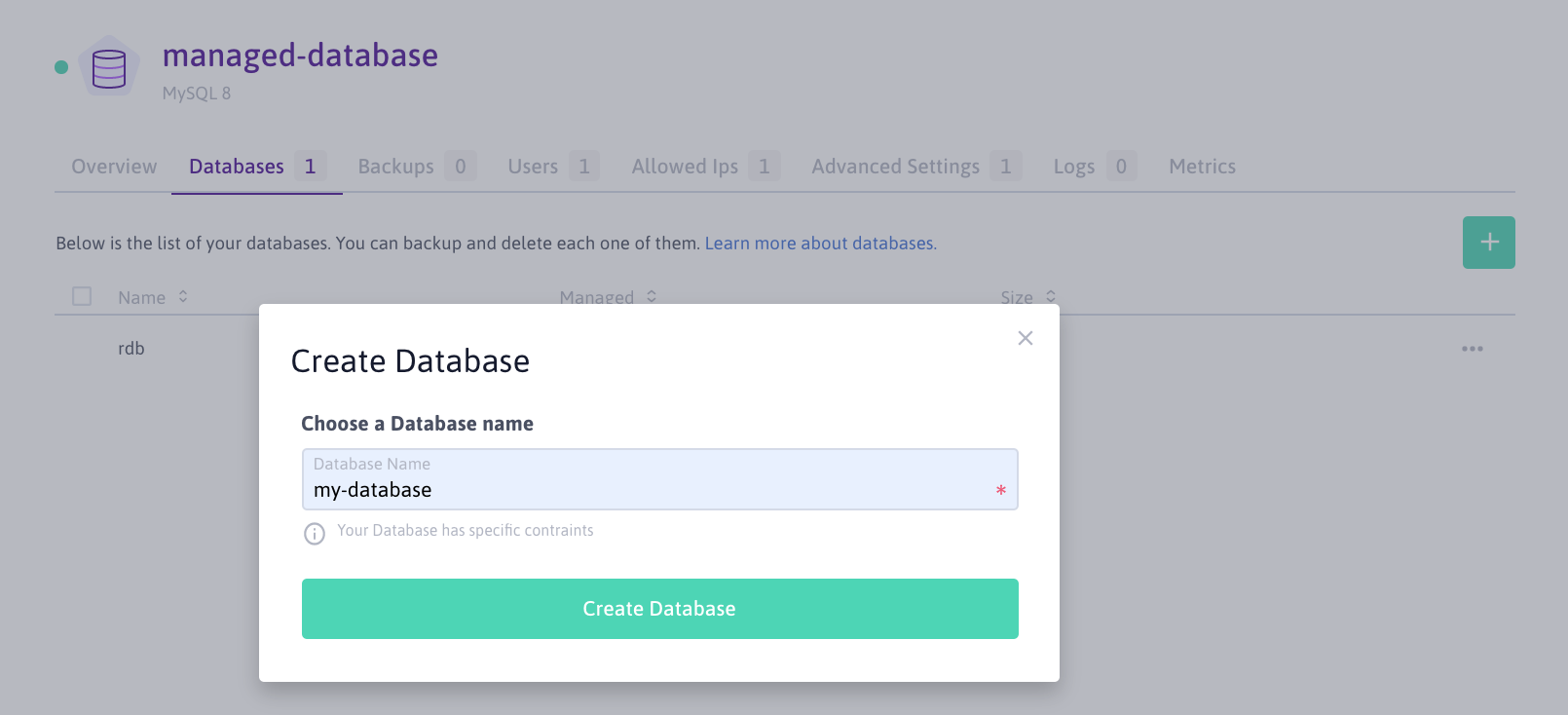
- Click the Managed Databases tab, then on + Create Database to create a new database in the instance.
- Enter the name of the new database and click Create Database to confirm the operation:
- Click the Users tab to visualize a list of all your database users. To create a new user for your database, click + Add user.
- Click the Permissions tab and grant
Allpermissions to your database for the user: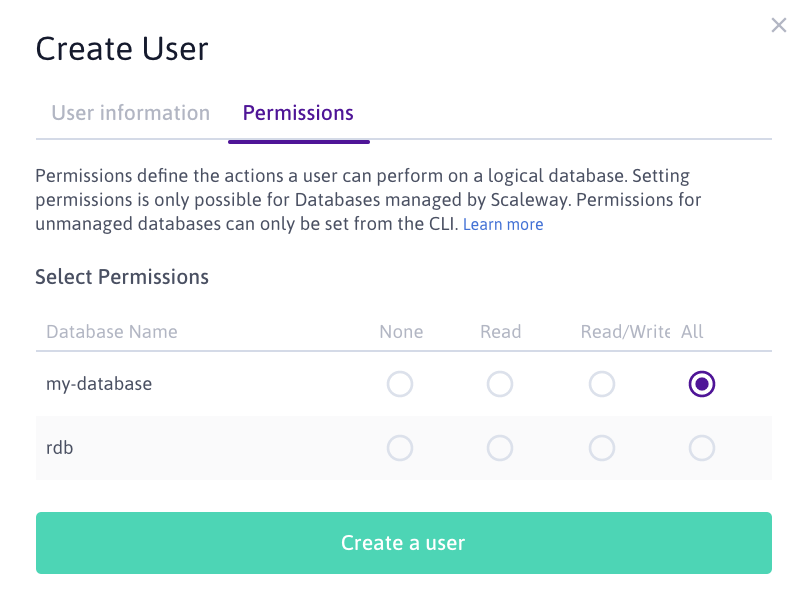
- Click the User Information tab and enter the credentials for the new user. Confirm by clicking on Create a user:
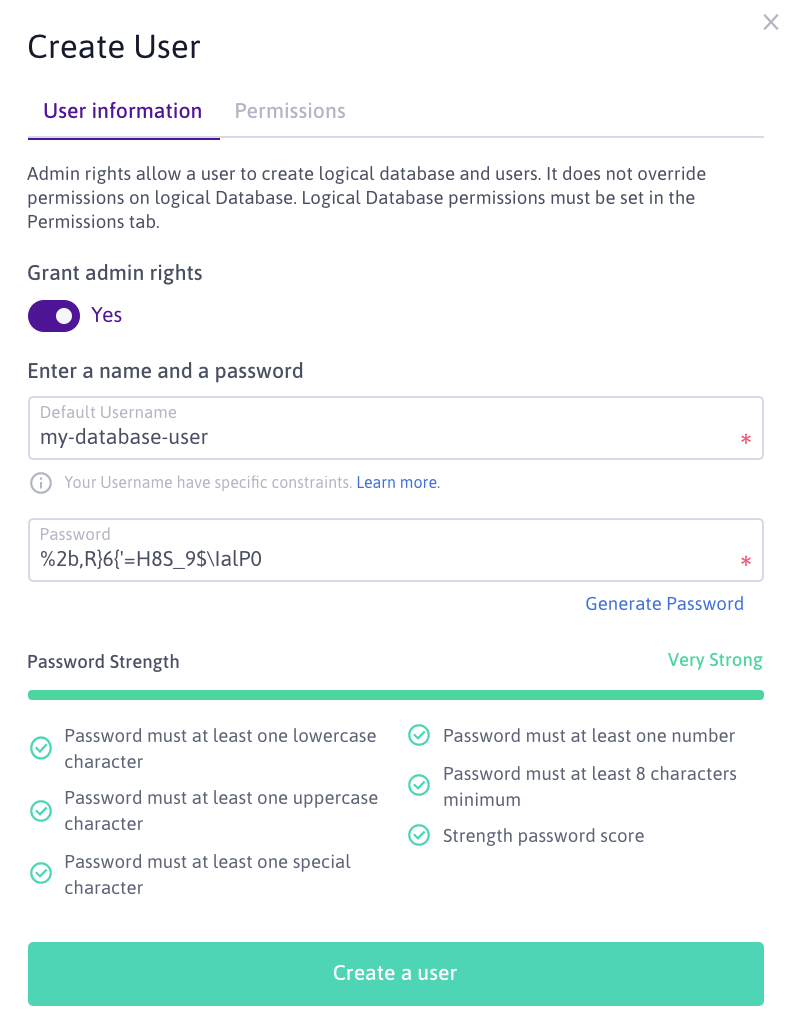
Importing the database
Once you have created both, the destination database and its users, import your data from the SQL file to your Database Instance by using the psql command-line tool.
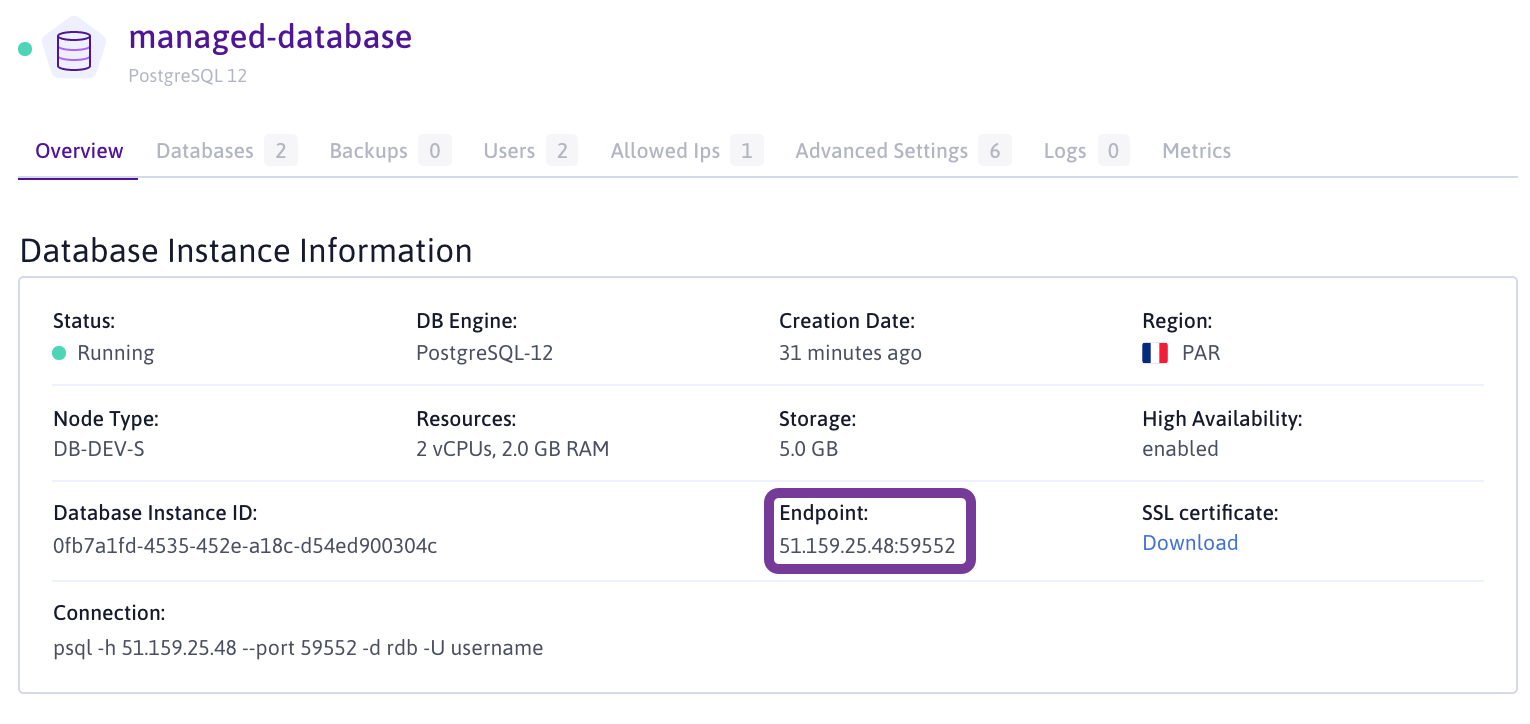
-
Retrieve the database host and port from your Scaleway console. The Endpoint information is visible on your Database information page:
-
Use the
psqlcommand-line tool to import your database with the following command:psql --file=<filename>.sql --host=<managed_database_endpoint_ip> --port=<managed_database_endpoint_port> --username=<user> --dbname=<database_nme>In the above command, replace the following values as follows:
<filename>: The file name of the exported database<managed_database_endpoint_ip>: The IP address of the Endpoint of your Database for PostgreSQL<managed_database_endpoint_port>: The TCP port of the Endpoint of your Database Instance<user>: The username for the Database<database_name>: the name of the Database
Database migration for MySQL
Exporting the source database
-
Connect to your Instance using SSH:
ssh root@<virtual_instance_ip> -
Update the
aptpackage cache and upgrade the software already installed on the system:apt update && apt upgrade -y -
We use
mysqldumpto dump the content of the database to migrate. It is included in the packagemysql-client. Install it using apt:apt install mysql-client -
Dump the content of the originating database into a local SQL file on the Instance:
mysqldump -P <port> -h <host> -u <user> -p <password> --opt <database_name> > <filename>.sqlIn the above command, replace the following values as follows:
<port>: The TCP port on which the database server is listening (by default3306)<host>: The database server hosting the MySQL database<user>: The username used for the connection to the database server<database_name>: The name of the database to export<filename>: The name of the local file of the exported database
Preparing the Database for MySQL
- Enter the Database section of the Scaleway console.
- Select your Database Instance from the list.
- Click the Managed Databases tab, then on + Create Database to create a new database in the instance.
- Enter the name of the new database and click Create Database to confirm the operation:
- Click the Users tab to visualize a list of all your database users. To create a new user for your database, click + Add user.
- Click the Permissions tab and grant
Allpermissions to your database for the user:
- Click the User Information tab and enter the credentials for the new user. Confirm by clicking on Create a user:

Importing the database
Once you have created both, the destination database and its users, import your data from the SQL file to your Database Instance by using the psql command-line tool.
-
Retrieve the database host and port from your Scaleway console. The Endpoint information is visible on your Database information page:
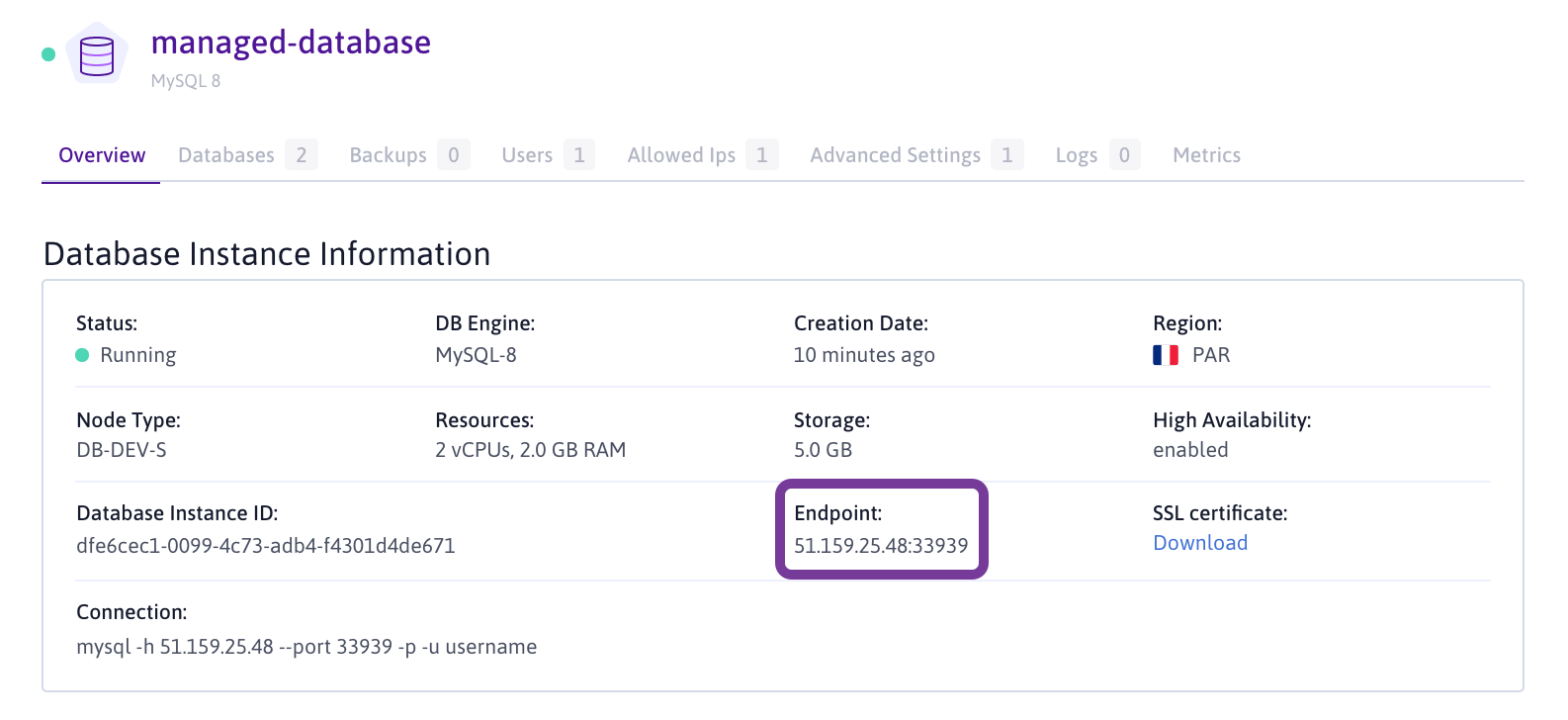
-
Use the
mysqlcommand-line tool to import your database with the following command:mysql -P <managed_database_endpoint_port> -h <managed_database_endpoint_ip> -u <user> -p <password> <database_name> < <filename>.sqlIn the above command, replace the following values as follows:
<managed_database_endpoint_port>: The TCP port of the Endpoint of your Database Instance<managed_database_endpoint_ip>: The IP address of the Endpoint of your Database for MySQL<user>: The username for the Database<password>: The password for the database user<database_name>: The name of the Database<filename>: The file name of the exported database
Conclusion
You now have exported your existing PostgreSQL or MySQL database and imported it into a Scaleway Managed Datatabase Instance. To finish the migration process of your database, update the credentials and server information in the configuration files of your existing application. Once this information is updated, your application will use your database on Instances managed by Scaleway. For more information about the Database product, refer to the product information page and the product documentation.
Visit our Help Center and find the answers to your most frequent questions.
Visit Help Center