How to create and manage ACLs
Access Control Lists (ACLs) allow you to control traffic arriving at your Load Balancer's frontend, and set conditions to allow traffic to pass to the backend, deny traffic from passing to the backend, or redirect traffic. Conditions can be set based on the traffic's source IP address and/or HTTP path and header, or you can choose to carry out unconditional actions. ACLs allow you to build extra security into your Load Balancer, as well as letting you redirect traffic, for example from HTTP to HTTPS.
Before you start
To complete the actions presented below, you must have:
- A Scaleway account logged into the console
- Owner status or IAM permissions allowing you to perform actions in the intended Organization
- Created a Load Balancer with a frontend
How to create ACLs
ACLs are created and managed at the frontend(s) of your Load Balancer.
-
Click Load Balancers in the Network section of the Scaleway console side menu. A listing of your Load Balancers displays.
-
Use the region selector at the top of the page to filter for the region of the Load Balancer you want to configure, then click the Load Balancer in the listing. The Load Balancer's Overview page displays.
-
Click the Frontends tab.
-
Click the name of the frontend you want to create ACLs for.
The Overview tab for the frontend displays.
-
Click the ACLs tab.

-
Click Create ACL or the plus icon button. The ACL creation wizard displays.

The first part of the wizard asks you to set a name and optional description for the ACL.
-
Enter the following information:
- ACL name: a name for your ACL.
- Priority: a priority number for your ACL. ACLs are applied in order of priority, starting from the lowest numbered rule.
- Description: an optional description for your ACL.
The second part of the wizard asks you to define the action for the ACL, and the conditions under which the action should be applied.
-
Select an action from the following options:
- Allow: Allow traffic to pass to the Load Balancer's backend.
- Deny: Deny traffic from passing to the Load Balancer's backend.
- Redirect: Redirect traffic to an alternative URI.
- Select a redirection code. The default value is
302. Other options are301,303,307or308. - Select a redirection URI option, from:
- Keep original: Redirect to the original URI.
- Select a scheme (HTTP or HTTPS) and port for the redirect.
- Define custom: Define a custom URI to direct to, in the format
https://{{host}}/{{path}}?{{query}}. Note that the only valid placeholder values are{{host}},{{path}}and{{query}}, and there must be no spaces between the curly braces and the string. You may use any, all or none of these placeholder values in your redirect URI.
- Keep original: Redirect to the original URI.
- Select a redirection code. The default value is
-
Use the Enable condition toggle to choose whether to set a condition for the action.
- If you do not enable a condition, the action will be applied uniformly to all traffic arriving at the Load Balancer's frontend.
- If you enable a condition, the action will be applied only to traffic meeting the condition you set below.
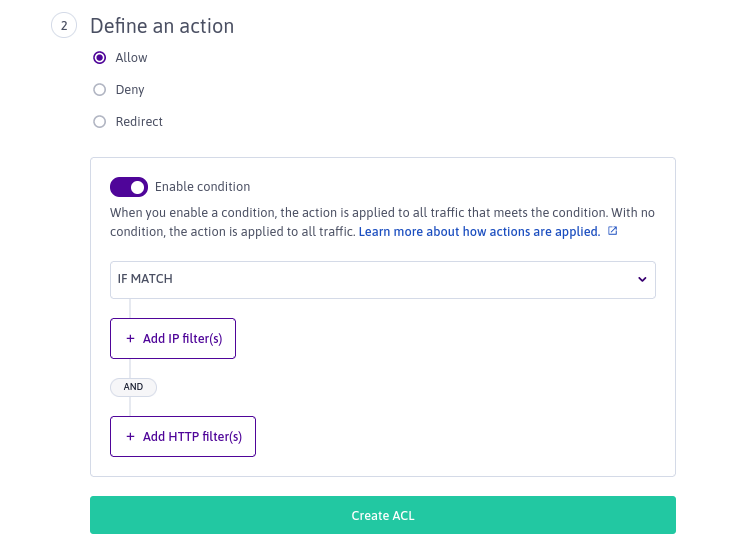
-
Set the condition type for your action, if you enabled a condition in the previous step. Choose from:
- IF MATCH: The action will be applied to all traffic that matches the filters (defined in the next step).
- IF NO MATCH: The action will be applied to all traffic that does not match the filters (defined in the next step).
-
Add filters, if you enabled a condition at step 8. Traffic must match (or not match, in the case of the IF NOT condition) the filters in order for the action to be applied. You can select one type of filter per ACL, or combine one IP filter and one HTTP header filter with an AND statement.
-
Click + Add IP filters to add an IP filter. Enter an IPv4 or IPv6 address (or IP block) in the box that displays, and click Add filter. You can repeat this step to add as many IP addresses as you like. Any traffic from the source IP addresses specified here will be considered to match the filter.
-
Click + Add HTTP filter(s) to add HTTP filters. Only frontends attached to an HTTP backend can add HTTP filters. You can select one of the following filter types per ACL:
- Path begins with: Enter a value to filter on, for example
/adminand click Add filter. Repeat this step to add multiple values to filter for, if required. Any traffic which has any of the specified values at the beginning of its HTTP request path will be considered to match the filter. - Path ends with: Enter a value to filter on, for example
/blogand click Add filter. Repeat this step to add multiple values to filter for, if required. Any traffic which has any of the specified values at the end of its HTTP request path will be considered to match the filter. - Path regex: Enter a regular expression to specify a pattern to search for in the HTTP request path, and click Add filter. Repeat this step to add multiple regex patterns to filter for, if required. Any traffic whose HTTP request path fits this regex will be considered to match the filter.
- Header: Enter the name of the HTTP header field to use for the filter, and the value to filter for in this header, then click Add filter. For example, enter
Refererfollowed byexampledomainto filter for occurrences ofexampledomainin theRefererheader. You can add multiple values to filter for if required but in only one header. Any traffic that has any of the specified values in the specified header field will be considered to match the filter.

- Path begins with: Enter a value to filter on, for example
-
-
Click Create ACL to finish. Your ACL is created, and you are redirected to the ACLs tab, where your new ACL now appears.
-
Repeat steps 5 to 11 to create new ACLs as required. Remember that they will be applied in order, according to the priority number you give each ACL.
How to edit ACLs
- Click Load Balancers in the Network section of the Scaleway console side menu. A listing of your Load Balancers displays.
- Use the region selector at the top of the page to filter for the region of the Load Balancer you want to configure, then click the Load Balancer in the listing. The Load Balancer's Overview page displays.
- Click the Frontends tab.
- Click the name of the frontend whose ACL(s) you want to edit. You are taken to the Overview tab for that frontend.
- Click the ACLs tab. The list of your ACLs displays.
- Click the more icon icon next to the ACL you wish to edit, and select Edit.
- Edit the ACL as required, and click Update ACL to finish.
How to delete ACLs
- Click Load Balancers in the Network section of the Scaleway console side menu. A listing of your Load Balancers displays.
- Use the region selector at the top of the page to filter for the region of the Load Balancer you want to configure, then click the Load Balancer in the listing. The Load Balancer's Overview page displays.
- Click the Frontends tab.
- Click the name of the frontend whose ACL(s) you want to edit. You are taken to the Overview tab for that frontend.
- Click the ACLs tab. The list of your ACLs displays.
- Click the more icon icon next to the ACL you wish to delete, and select Delete.
- Confirm the action by clicking Delete ACL.